
Odoo (previously known as OpenERP) is a collection of open source Business applications. The most utilized components or modules for Odoo are Point of Sale (POS), Stock, CRM, Website, Live Chat, eCommerce, Invoicing, Accounting, Warehouse, etc.
The variety of components or modules that can be implemented in one application makes Odoo so widely used nowadays. In this guide, we will demonstrate how to Install Odoo on Debian 12.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
- A Debian 12 VPS with at least 2GB of RAM.
- SSH access with sudo privileges or root access.
Step 1. Login and Update the System
First of all, we need to log in to our Debian 12 VPS through SSH:
ssh root@IP_Address -p Port_number
You will need to substitute ‘IP_Address’ and ‘Port_number’ with your server’s corresponding IP address and SSH port number. Furthermore, substitute ‘root’ with the username of the system user with sudo privileges.
Once logged in, we can run this command
# lsb_release -a
You should see this as the output:
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Debian
Description: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm)
Release: 12
Codename: bookworm
To make sure the system packages are up to date, let’s run this command:
# apt update -y
Step 2. Install Dependencies
Before starting, we will install the dependencies on our Debian 12 system. Let’s execute the command below to proceed.
apt install build-essential wget git python3-pip python3-dev python3-venv \
python3-wheel libfreetype6-dev libxml2-dev libzip-dev libsasl2-dev \
python3-setuptools node-less libjpeg-dev zlib1g-dev libpq-dev \
libxslt1-dev libldap2-dev libtiff5-dev libopenjp2-7-dev
Step 3. Create a System User
After installing the dependencies, we will now create a new system user and grant it with sudo privileges. We will also use this user to complete this installation. In this tutorial, we will create a new system user called ‘odoo’, you can choose any username you like and make sure it matches with the PostgreSQL user we will create in the next step.
adduser \ --system \ --shell /bin/bash \ --gecos 'Odoo user' \ --group \ --home /opt/odoo \ odoo
Step 4. Install PostgreSQL Server
Odoo only supports PostgreSQL to store its data. Let’s execute the command below to install the PostgreSQL server on our Debian 12 server.
# apt install postgresql
After the installation is finished, we can add a new postgresql user for our Odoo instance; run this command:
# su - postgres -c "createuser -s odoo"
Step 5. Install wkhtmltopdf
Wkhtmltopdf is an open-source command line tool to render HTML data into PDF format using Qt webkit. To install wkhtmltopdf on your Debian 12 server, execute the command below.
# apt install wkhtmltopdf
To check the wkhtmltopdf version, we can execute the command below.
# wkhtmltopdf --version
Step 6. Install Odoo
There are some options to install Odoo on a Debian 12 server. In this post, we will install Odoo using a Python virtual environment. This way, we can host multiple Odoo instances on our server and they will not share the same Python packages. Odoo will be installed under user ‘odoo’ we created earlier. Let’s switch to the user and start the installation.
# su - odoo
$ git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 16.0 odoo16
The command above will download Odoo files onto /opt/odoo/odoo16 directory. Now, let’s create a python virtual environment.
$ python3 -m venv odoo16-venv
Python virtual environment is installed on /opt/odoo/odoo16-venv directory, now we need to activate it
$ source odoo16-venv/bin/activate
Once invoked, your shell prompt would look like this:
(odoo16-venv) odoo@rh:~$
Next, let’s install Odoo
(odoo16-venv) odoo@rh:~$ pip3 install wheel
(odoo16-venv) odoo@rh:~$ pip3 install -r odoo16/requirements.txt
At this point, Odoo and its required Python packages have been successfully installed.
The next step is to create an odoo custom addons directory. We can use this directory to store our custom Odoo modules.
$ mkdir /opt/odoo/odoo16/custom-addons/
Then, deactivate the virtual environment exit from odoo user and get back to root to create the odoo configuration.
$ deactivate && exit
Let’s create an Odoo configuration file.
# nano /etc/odoo16.conf
Insert the following into the file
[options] admin_passwd = m0d1fyth15 db_host = False db_port = False db_user = odoo db_password = False addons_path = /opt/odoo/odoo16/addons,/opt/odoo/odoo16/custom-addons xmlrpc_port = 8069
Save the file and exit from the editor
Step 7. Create Odoo Systemd File
It is time to create a systemd unit file; it is required to start/stop/restart Odoo service.
# nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo16.service
Paste the following content into the systemd unit file above.
[Unit] Description=Odoo16 Requires=postgresql.service After=network.target postgresql.service [Service] Type=simple SyslogIdentifier=odoo16 PermissionsStartOnly=true User=odoo Group=odoo ExecStart=/opt/odoo/odoo16-venv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo/odoo16/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo16.conf StandardOutput=journal+console [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
That’s it. We can now reload systemd and run Odoo.
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl start odoo16
Check if Odoo is starting by running this command:
# systemctl status odoo16
Open your web browser and navigate to http://YOUR_SERVER_IP_ADDRESS:8069; you will see the Odoo page
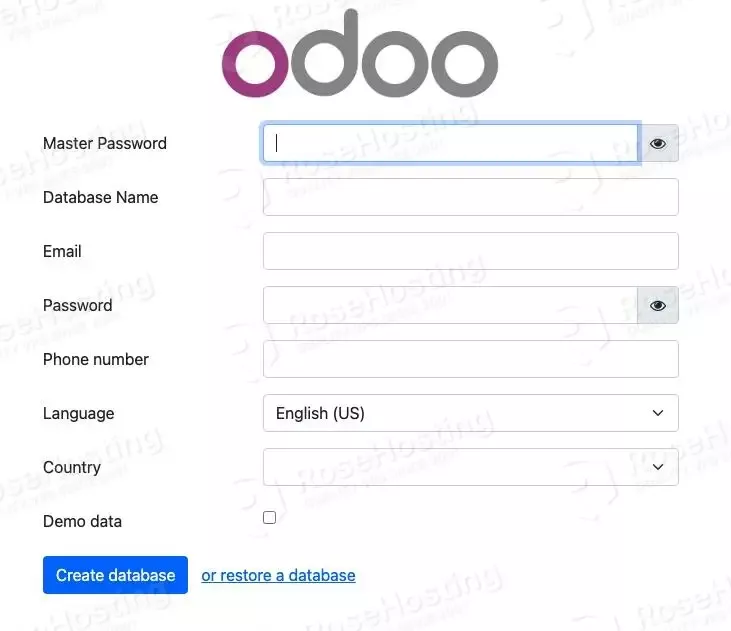
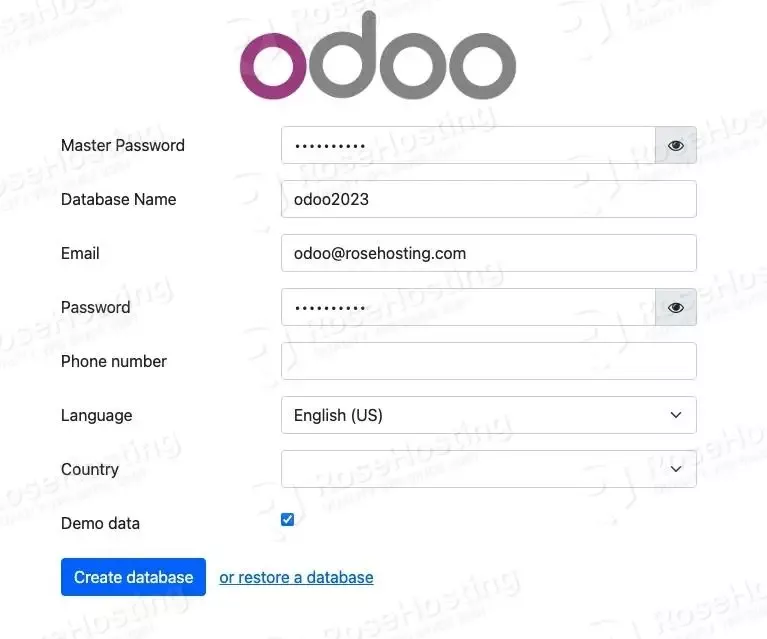
On this page, you can create a new Odoo database. Use the admin_passwd in /etc/odoo16.conf file as the Master Password and fill in all others before hitting the ‘Create database’ button. Make sure to save a copy of the email and password; you will use them to log in to the Odoo backend later.
Then, you will be brought to the login page.
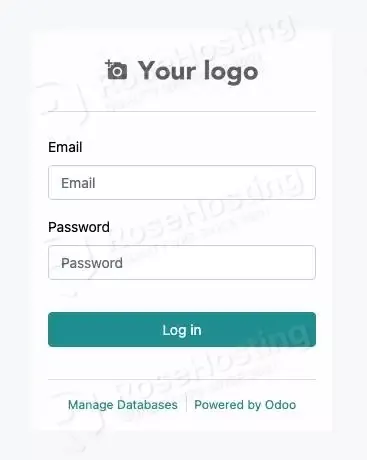
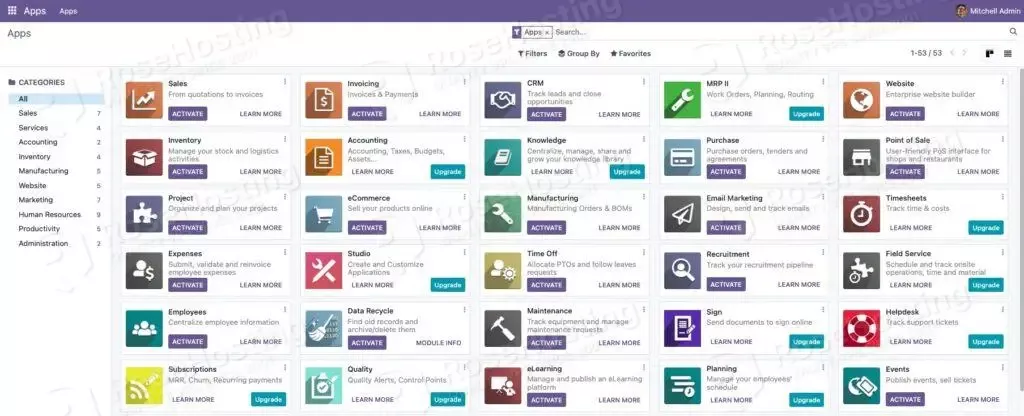
Use the email and password when creating a new database in the previous step to log in and access the backend.
To enable and automatically start Odoo upon server reboot, we need to invoke this command.
# systemctl enable odoo16
Step 8. Install and Configure Nginx
At this point, we are able to access Odoo at http://YOUR_SERVER_IP_ADDRESS:8069. It would be easier if we can access Odoo at http://ourdomain.com instead. So, in this step, we will configure nginx as the reverse proxy to Odoo. Simply install nginx from the default Debian 12 repository.
# apt -y install nginx
Upon installation, nginx will start, and it’s already configure to start on boot automatically.
Now, we will create an Nginx server block for the domain name we will use for accessing Odoo. For example, we will use ourdomain.com
# nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ourdomain.com.conf
Insert the content below into the file.
upstream odoo16 {
server 127.0.0.1:8069;
}
upstream odoochat {
server 127.0.0.1:8072;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name ourdomain.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.error.log;
proxy_buffers 16 64k;
proxy_buffer_size 128k;
location / {
proxy_pass http://odoo16;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
}
location /longpolling {
proxy_pass http://odoochat;
}
location ~* /web/static/ {
proxy_cache_valid 200 60m;
proxy_buffering on;
expires 864000;
proxy_pass http://odoo16;
}
}
Save the file and restart the web server for the changes to take effect
# systemctl restart nginx
Now you should be able to access Odoo with your domain name at http://ourdomain.com and start working on your project. Learn how to secure your Odoo website using an SSL/TLS certificate.
Of course, you don’t have to install Odoo on Debian 12 if you have an active VPS hosting service with us, in which case you can simply ask our expert Linux admins to install Odoo on Debian 12 for you. They are available 24×7 and will take care of your request immediately.
PS. If you liked this post about installing Odoo on Debian 12, please share it with your friends on social networks using the buttons below or simply leave a comment in the comments section. Thanks.