Status: Deprecated
This article, “Install Squid on Debian 6,” covers a version of Debian 6 that reached end of life in 2016. As it’s no longer supported, this guide is no longer maintained. If you are currently operating a server running Debian 6, we highly recommend contacting RoseHosting’s fully managed support. We can upgrade or migrate you to a supported version of Debian.

Table of Contents
Squid Installation
apt-get update apt-get install squid
Squid Configuration
Open the squid3 configuration file and add the following lines under the http_access block, right after the “# INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS” line.
nano /etc/squid/squid.conf acl mynet src 192.168.0.23 http_access allow mynet visible_hostname your.domain.com
Where ‘192.168.0.23’ is your local computer’s IP address.
Restart the squid service:
/etc/init.d/squid restart
Browser Configuration
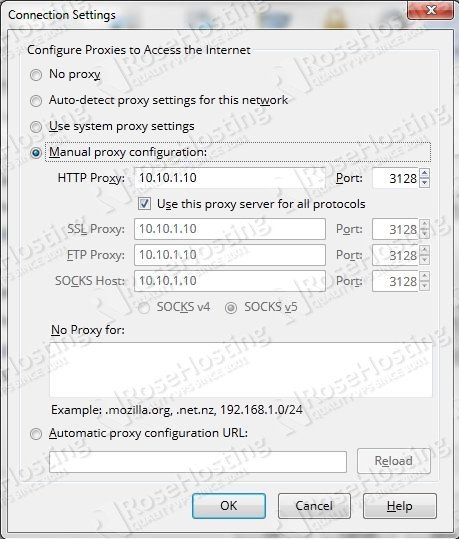
In Firefox, go to Options -> Advanced -> Network -> Connection and then click on the Settings button.
Where ‘10.10.1.10’ is the IP address of your Debian VPS.
PS. If you liked this post, please share it with your friends or leave a reply below. Thanks.