Nagios3 is a robust and very powerful monitoring system which can help you monitor your virtual servers and the services running on your servers.
It is one of the best open-source monitoring systems out there.
Before proceeding any further, initiate a screen session by executing:
## screen -U -S nagios-screen
Then, make sure your Ubuntu 13.10 VPS is fully up-to-date by executing:
## apt-get update ## apt-get upgrade
If Apache2 is not installed on your vps, run the command below to install it:
## apt-get install apache2
Next thing to do, is to install Nagios and Nagios NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) Plugins on your VPS by running:
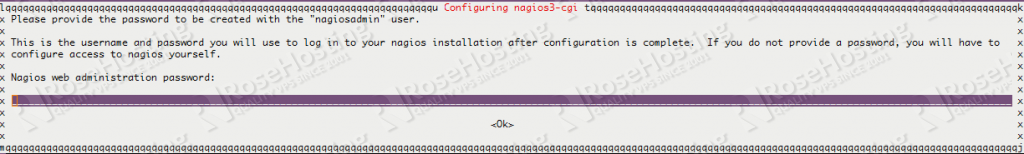
## apt-get install nagios3 nagios-nrpe-plugin
you should be prompted to enter your nagiosadmin user’s password as shown below
if for some reason you’re not, then use the following command to set your nagiosadmin user’s password:
## htpasswd -c /etc/nagios3/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
proceed with adding Apache’s www-data user to the nagios group:
## usermod -a -G nagios www-data
add executable bit for nagios group to everything under the /var/lib/nagios3/ directory:
## chmod -R g+x /var/lib/nagios3/
next, edit Nagios3 configuration file in /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg and enable external commands by setting check_external_commands from 0 to 1:
## vim +/check_external_commands /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
restart Nagios and Apache and access your Nagios at http://your.hostname.com/nagios3
## service apache2 restart ## service nagios3 restart
Adding servers or services to nagios is done by creating a configuration file for a particular host. In this case, lets monitor a CentOS VPS (my.hostname.com) and some of the services running on it from your Nagios. So, create a configuration file for this VPS:
## cd /etc/nagios3/conf.d ## vim my.hostname.com.cfg
and add the following:
define host {
use generic-host
host_name my.hostname.com
alias host-cosini
address XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name my.hostname.com
service_description HTTP
check_command check_http
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name my.hostname.com
service_description SSH
check_command check_ssh!2219!
notifications_enabled 0
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name my.hostname.com
service_description PING
check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60%
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name my.hostname.com
service_description LOAD
check_command check_nrpe_1arg!check_load
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name my.hostname.com
service_description FTP
check_command check_nrpe_1arg!check_ftp
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name my.hostname.com
service_description DISK
check_command check_nrpe_1arg!check_storage
}
save and close the file and restart nagios3 for the changes to take effect:
## service nagios3 restart
access http://your.hostname.com/cgi-bin/nagios3/status.cgi?host=all
and see if the new server is shown in the interface.
In order to monitor some of the services running on our client CentOS 6 VPS, we need to install and configure NRPE on the server. To do that, first we need to enable the EPEL repository and install the packages by:
## rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm ## yum install nrpe nagios-plugins-all
once installed, we need to configure NRPE by editing /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg:
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1 change to allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
where XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX is your Nagios VPS IP address
add/edit the following command:
command[check_ftp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -a proftpd command[check_storage]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /
enable NRPE on system start-up and start the service:
## chkconfig nrpe on ## service nrpe start
Of course, if you are one of our Linux VPS Hosting customers, you don’t have to do any of this, simply ask our admins, sit back and relax. Our admins will set this up for you immediately. For more updates, you can also read our guide on How to install Nagios3 and Check_MK on an Ubuntu 12.04 LTS VPS.
PS. If you liked this post please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons on the left or simply leave a reply below. Thanks.